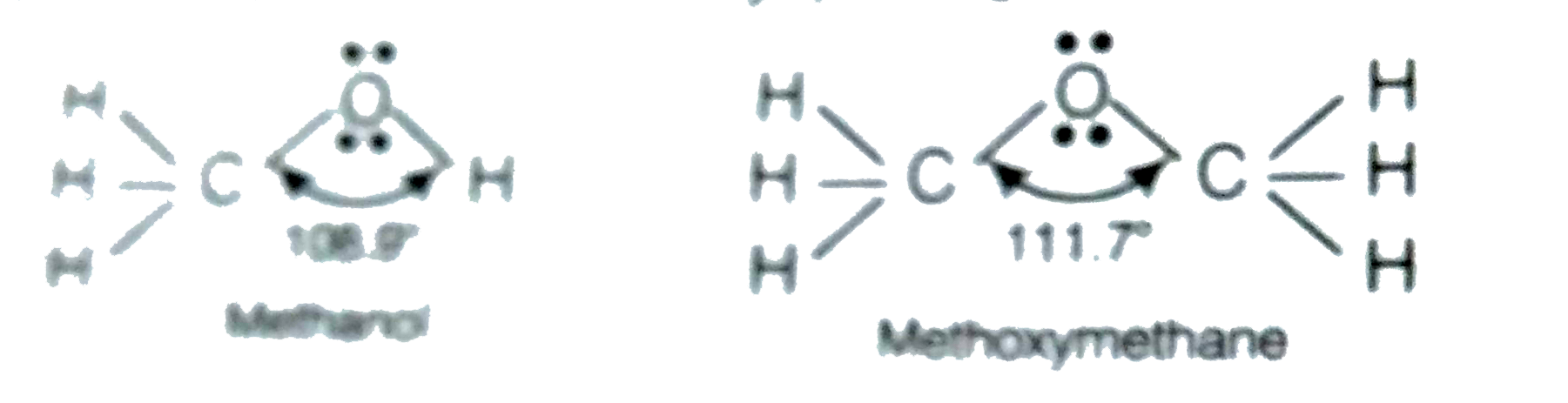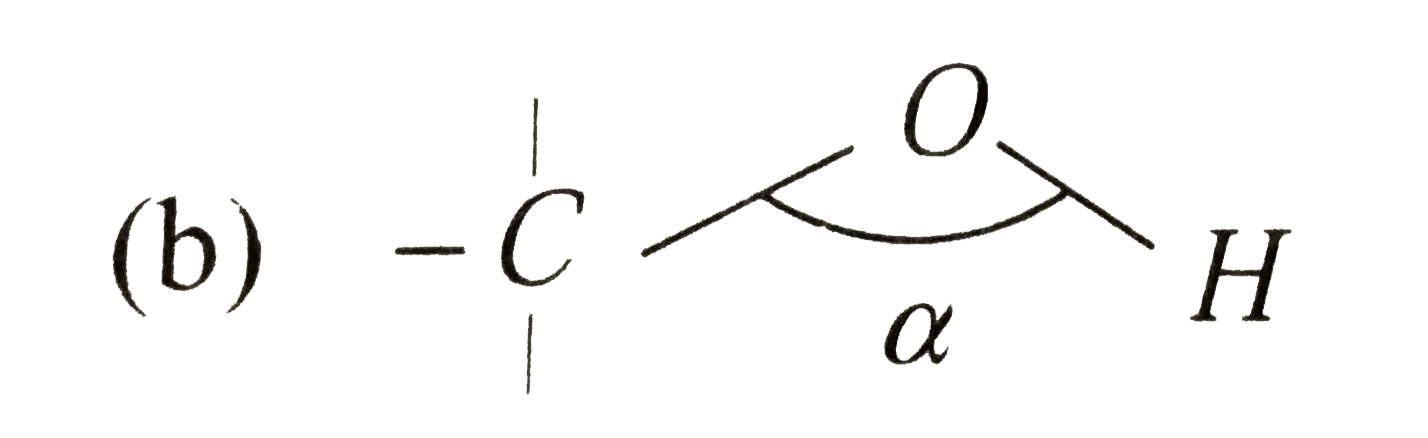C O H Bond Angle In Alcohol Is Less Than Tetrahedral Angle

Therefore three is comparatively more repulsion and less and angle.
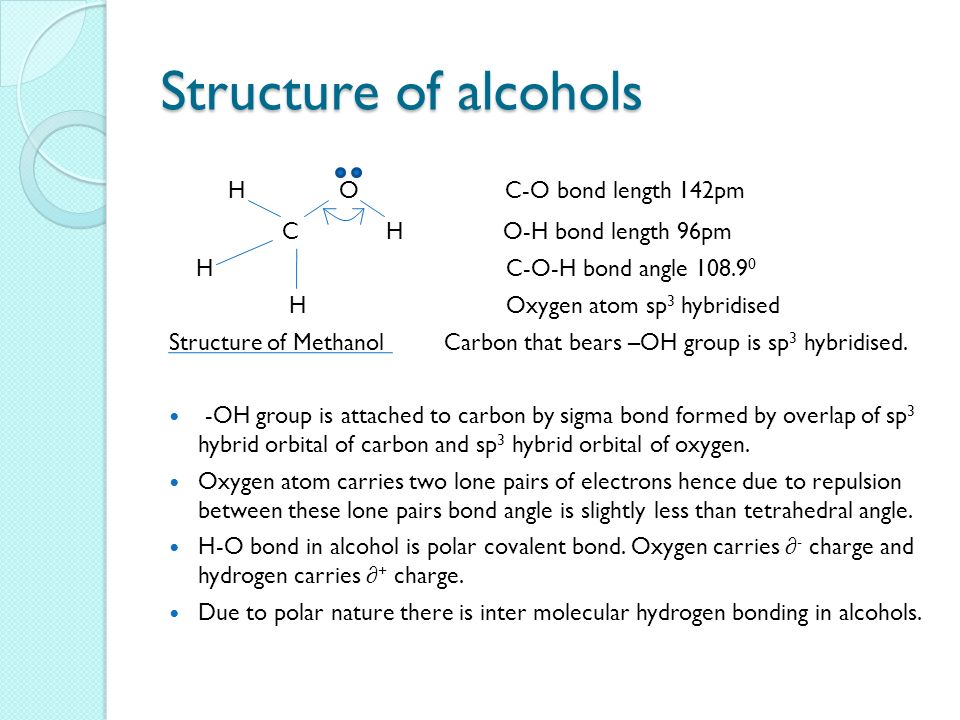
C o h bond angle in alcohol is less than tetrahedral angle. Br the bond angle in their slightly greater than the tetrahderal angle due to the repulsive interaction between the two bulkyl r groups. Coh bond angle in alcohol is less than tetrahedral angle of 109 50 coc bond angle in ether is more than tetrahedral angle of 109 50. The bond angle in in alchols is slightly less than tetrahedral is slightly less than tetrahedral angle. It is due to the repulsion between the unshared electron pairs of oxygen.
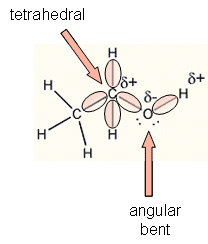
The c o h bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle due to the repulsion between the unshared pair of electrons or the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom. In both the cases oxygen atoms contain two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons and are oriented in a tetrahedral shape around the oxygen atom. In a perfect tetrahedral like ch4 all four hydrogen groups are distributed around the carbon atom equally leading to the bond angle of 109 5 deg. Therefore three is comparatively more repulsion and less and angle.
H in alchols is slightly less than tetrahedral is slightly less than tetrahedral angle 109 28. However in the case of the oxygen atom in an alcohol i assume that s the bond angle you are looking at the substituents on the oxygen are a carbon atom a hydrogen atom and two lone pairs. It is due to the repulsion between the unshared electron pairs of oxygen. This results in the bond angle slightly greater than the tetrahedral angle.
The c o h bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle whereas the c o c bond angle in ether is slightly greater because of repulsion between the two bulky r groups. In case of ethers the oxygen atom is surrounded by bulky alkyl groups hence repulsion between these r groups pushes the two c o bonds away from each other and hence the bond angle is slightly greater than the tetrahedral angle. The c o h bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle because of the repulsion between the two lone pairs of electrons on oxygen atoms as these pairs pushes the c o bonds closer to each other. In alcohols two lone pair of electrons are present.